Continuing military, financial, and humanitarian aid to Ukraine is a strategic investment that enhances global stability and safeguards U.S. national interests.
Stimulating the U.S. Economy
Since February 2022, Congress has allocated approximately $113.3 billion in aid to Ukraine across four major packages. A significant portion of this funding directly benefits the U.S. economy:
- Domestic Production: Funds are used within the U.S. to manufacture weapons and ammunition, driving economic growth and job creation. These resources are distributed among American defense contractors and taxpayers as wages, keeping the money circulating within the U.S. economy.
- Increased Exports: The effective use of American weapons in Ukraine has heightened global demand for U.S. defense products, boosting exports and solidifying the competitiveness of American defense companies in international markets.
Cost-Effective Defense of NATO and U.S. Interests
Financial support for Ukraine is significantly cheaper than the potential costs of deterring Russia in the event of its victory. Without Ukrainian resistance:
- Higher Defense Spending: The U.S. would need to increase military budgets and deploy forces in Europe to counter an emboldened Russia.
- Deterrence of Aggression: Supporting Ukraine aligns with “Make America Great Again” principles by asserting Washington’s leadership in upholding international norms and preventing the spread of conflict.
Strengthening NATO and Mitigating Future Threats
- Reinforcing NATO’s Eastern Flank: Weakening Russia through Ukraine strengthens NATO’s eastern front, reducing risks for Alliance members and minimizing the need for large-scale U.S. troop deployments in Europe.
- Preventing Escalation: A weakened Russian military lowers the likelihood of aggression against Baltic nations, avoiding scenarios where U.S. forces might be drawn into direct conflict under NATO’s collective defense commitments.
Enhancing U.S. Military Readiness
The conflict in Ukraine provides a real-world testing ground for modern weapons, tactics, and defense concepts:
- Innovation in Warfare: The war has allowed the U.S. to evaluate the performance of advanced systems, such as electronic warfare equipment against drones and armored units operating under drone surveillance.
- Defense Sector Modernization: Increased production to support Ukraine is accelerating the modernization of the American defense industry, ensuring preparedness for future challenges.
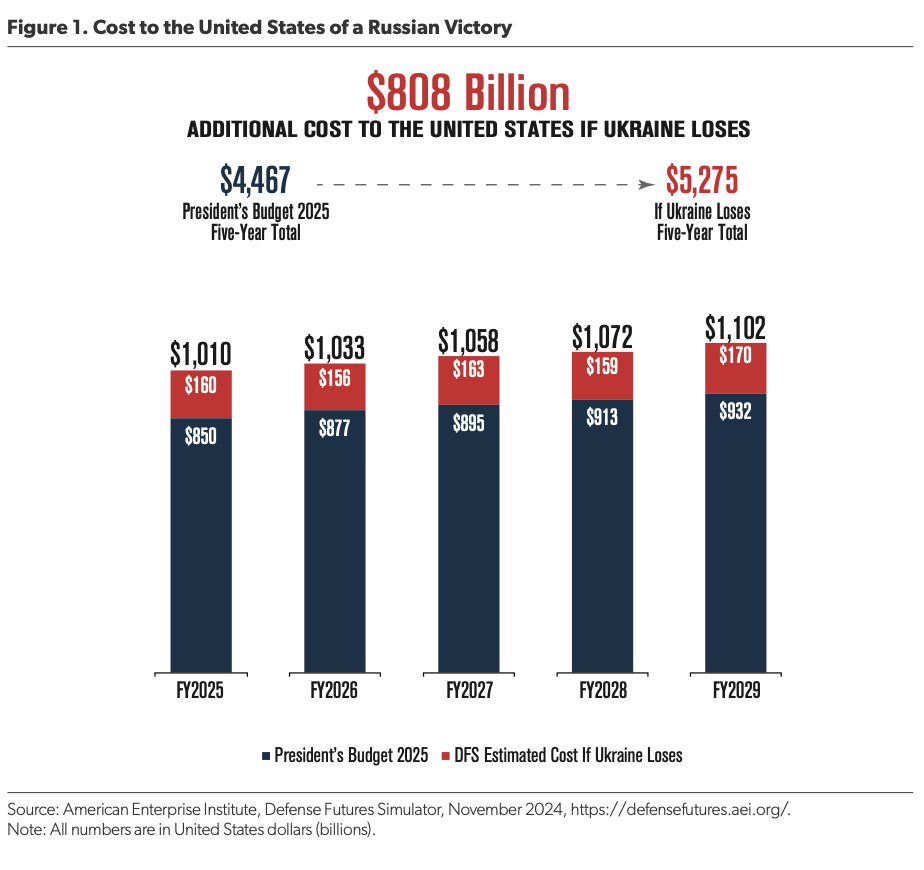
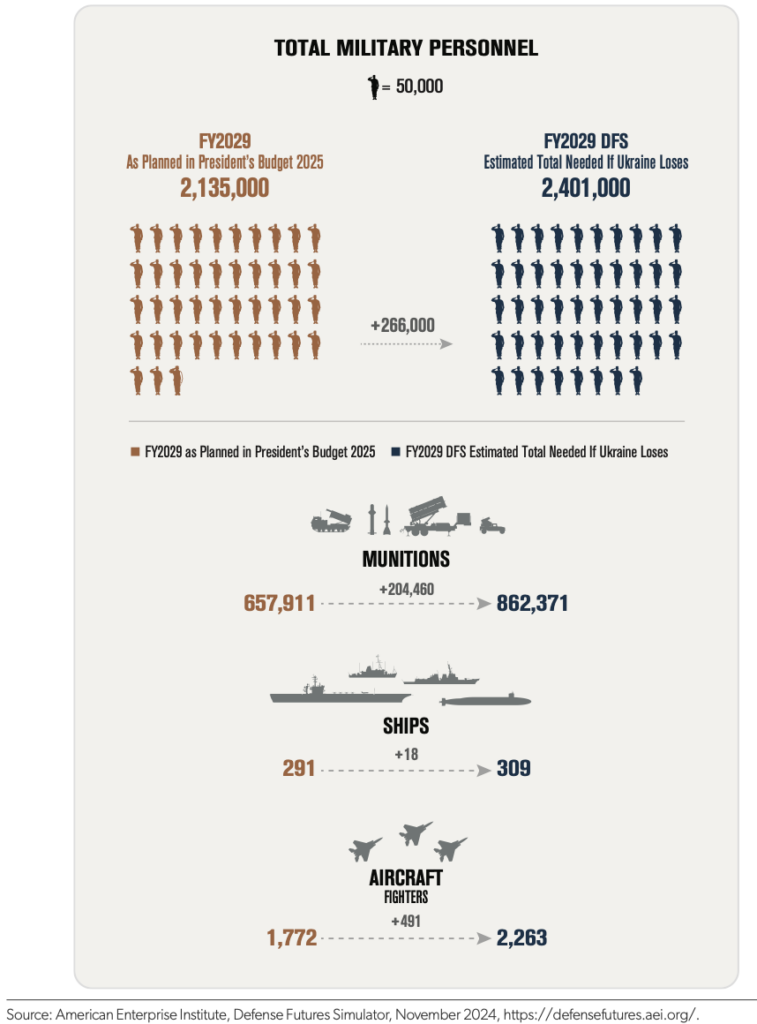
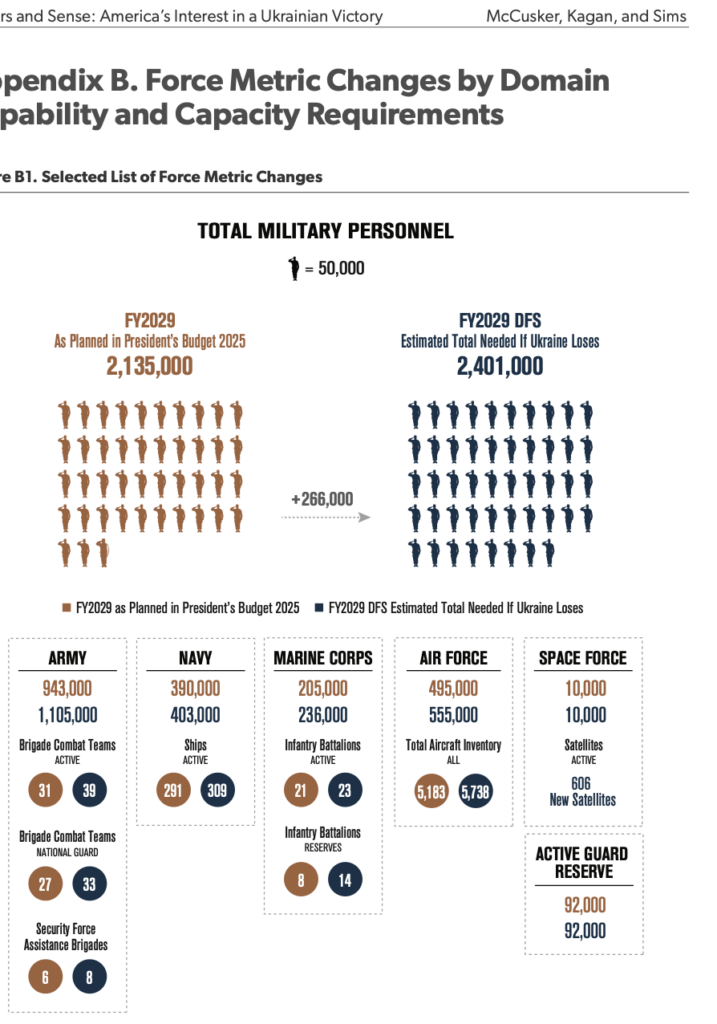
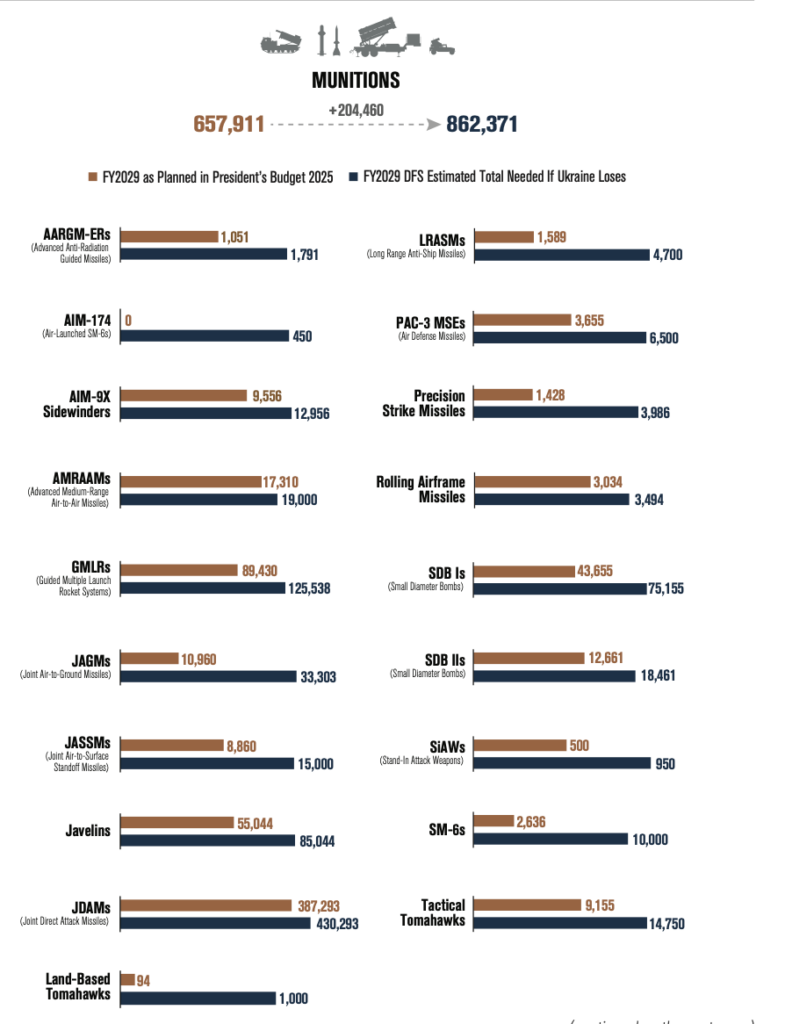
If Ukraine were to be defeated, the additional costs to the United States would amount to an estimated $808 billion over the next five years. This scenario underscores the financial prudence of continuing support for Ukraine to avoid these far-reaching expenditures. Below is a detailed breakdown of projected costs under current plans versus the scenario of Ukraine’s defeat:
Supporting Ukraine remains a profitable investment for the United States, yielding economic advantages, reinforcing national security, and maintaining the international order. By sustaining aid, the U.S. ensures a favorable balance of power globally while securing its leadership role and bolstering domestic economic and military capabilities.
The Effectiveness of U.S. Military Aid to Ukraine: A Comparative Analysis with Aid to Afghanistan During Donald Trump’s First Term
The effectiveness of U.S. military aid to Ukraine is evident when compared to similar assistance provided to Afghanistan during Donald Trump’s first presidency (2017–2021). While both nations received significant support, the outcomes differ starkly due to variations in geopolitical context, governance, and the nature of U.S. involvement.
During Trump’s presidency, U.S. military aid to Ukraine and Afghanistan differed significantly in both scale and effectiveness. Ukraine received substantial military aid, especially in the form of lethal assistance like Javelin missiles, aimed at countering Russian aggression. In contrast, military aid to Afghanistan continued at high levels but was ultimately ineffective in ensuring long-term stability, largely due to systemic issues within the Afghan military and the broader political context. The shift in U.S. policy toward withdrawal from Afghanistan further limited the effectiveness of the aid provided to Afghan forces.
During Donald Trump’s first presidency (2017-2021), the U.S. military aid to Ukraine and Afghanistan was notable, but the amounts, focus, and effectiveness of the aid varied significantly between the two countries.
Military Aid to Ukraine (2017-2021)
Amount of Aid
- Total Aid: Under Trump, U.S. military aid to Ukraine increased significantly compared to the Obama administration. From 2017 to 2021, the U.S. provided more than $2.5 billion in military assistance to Ukraine. This was a marked increase from previous years, especially during the Obama administration when aid was more limited.
- Types of Aid: The aid included:
- Lethal Aid: In 2017, the Trump administration approved the provision of Javelin anti-tank missiles to Ukraine, marking a significant shift from the Obama administration, which had only provided non-lethal aid (such as body armor, medical supplies, and training).
- Training and Advisory: The U.S. provided military training and advisory support to Ukrainian forces, including counterinsurgency training and battlefield medical training.
- Tactical Equipment: Other supplies included radars, drones, and medical evacuation equipment.
Effectiveness of Aid
- Strengthening Ukraine’s Military: The military aid provided under Trump helped improve Ukraine’s defensive capabilities, particularly in countering Russian-backed separatists in the Donbas region. The Javelin missiles were seen as an important tool for Ukraine to deter Russian armor and provide a symbolic boost to Ukrainian morale.
- Political Support: Trump’s support for Ukraine, particularly through military aid, signaled a shift in U.S. foreign policy toward more direct assistance in the conflict with Russia, which had been ongoing since Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Military Aid to Afghanistan (2017-2021)
Amount of Aid
- Total Aid: The U.S. continued to provide extensive military aid to Afghanistan during Trump’s presidency, although the total amount of aid declined as the administration moved toward a policy of eventual withdrawal. By 2021, the U.S. had spent more than $80 billion on Afghan security forces since 2001, with significant portions of this funding occurring during Trump’s presidency.
- Types of Aid:
- Weapons and Equipment: This included rifles, helicopters, and tactical vehicles for the Afghan National Army (ANA) and the Afghan National Police (ANP).
- Training and Support: The U.S. continued to provide training and advisory support, with U.S. military personnel embedded within Afghan forces to offer guidance.
- Air Support: The U.S. provided air support to Afghan forces, including airstrikes and intelligence sharing.
Effectiveness of Aid
- Military Capability: The military aid helped sustain Afghan security forces, but it was often undermined by a lack of long-term sustainability and dependence on U.S. support. Despite U.S. investments, Afghan forces struggled with corruption, low morale, and a lack of cohesion, which hampered their ability to secure the country effectively.
- Increased Taliban Resurgence: By the time Trump left office, the Taliban had regained significant territory, demonstrating that the military aid, while substantial, had not been sufficient to ensure long-term stability in Afghanistan. The failure of Afghan forces to maintain control over large parts of the country was partly due to a lack of will and effectiveness at the local level.
- Shift in Policy: Trump’s administration pursued a policy of reducing U.S. military involvement, culminating in the Doha Agreement in 2020, which outlined a timeline for the withdrawal of U.S. troops. This reduction in support contributed to the rapid collapse of the Afghan government and military in 2021.
- Ukraine: Ukraine’s conflict with Russia was seen as a critical geopolitical struggle for Europe and global stability. Russia’s annexation of Crimea and its involvement in eastern Ukraine posed a direct challenge to European security and NATO interests. As a result, the U.S. provided more direct and meaningful military aid to Ukraine, especially under Trump’s policy of countering Russian aggression.
- Afghanistan: Afghanistan was viewed more as a long-term, complex counterinsurgency and nation-building operation. By the time Trump took office, there was a growing recognition that the war in Afghanistan had become protracted and that a military solution was unlikely. The focus of U.S. policy shifted towards a negotiated settlement with the Taliban, leading to a gradual reduction in military aid and a shift toward diplomatic solutions.
Trump’s Approach to Foreign Policy
- Ukraine: Trump’s approach to Ukraine was characterized by a pragmatic interest in countering Russian influence, though it was often clouded by his personal dealings with Russia and the impeachment scandal. Nonetheless, the U.S. increased military aid to Ukraine, albeit with some inconsistencies due to political pressures.
- Afghanistan: Trump was committed to reducing U.S. involvement in endless wars, and Afghanistan was the focal point of his “America First” policy, which prioritized withdrawal over long-term military commitments. His administration signed the Doha Agreement with the Taliban, which set in motion the withdrawal of U.S. troops and a scaling down of military aid.
Effectiveness of Trump’s Policies
- Afghanistan: Despite substantial military aid, the effectiveness in Afghanistan was limited by the failure of the Afghan government to effectively use the support and by the ongoing instability caused by corruption, poor leadership, and the strength of the Taliban. The U.S. military’s eventual withdrawal in 2021, under Trump’s policy, led to the rapid collapse of the Afghan government.




